Make
Donation

THANK TO THE RESULTS ACHIEVED WITH YOU !
6893
HELPED PEOPLE
6893
HELPED PEOPLE
Hear The World
Like Never Before!
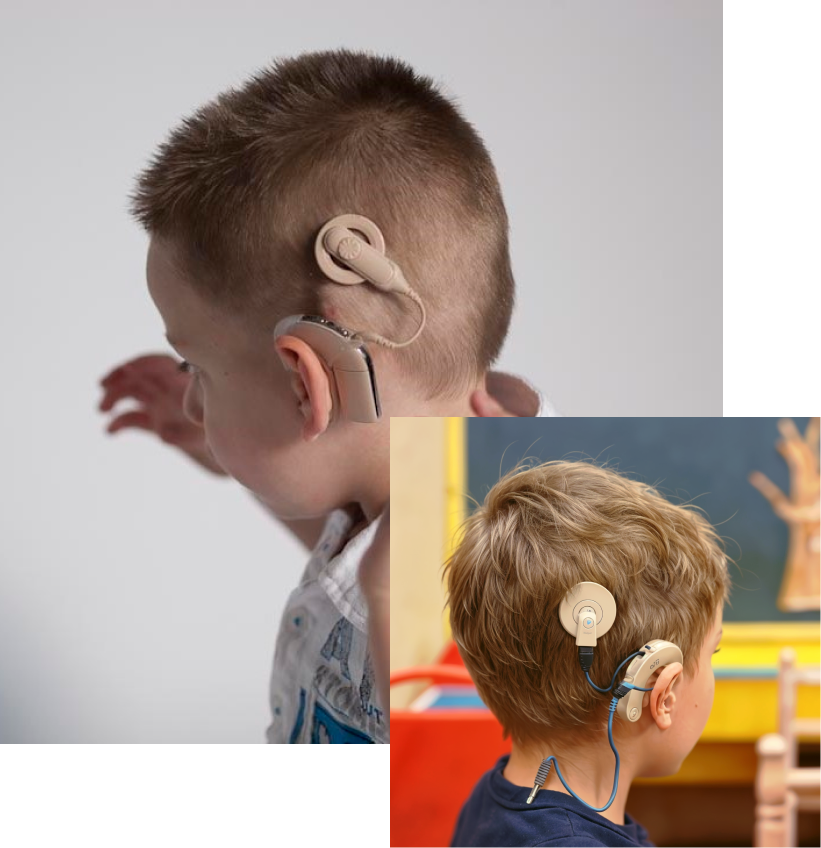
ABOUT US
CIACS
The Cochlear Implantees Association and Charitable Society was Established in 2016. At CIASC, we always start with people in mind, thinking about their needs. We stand as a beacon of resilience, unity, and empowerment within the community of those whose lives have been profoundly impacted by cochlear implants
From the very outset, our organization has been dedicated to rewriting narratives and amplifying voices that were once muted by hearing impairments.
With a steadfast commitment to fostering hope and facilitating holistic support, we have become a vibrant community where individuals with cochlear implants find not just assistance, but a profound sense of belonging. Over the years, we have tirelessly championed the cause of breaking down communication barriers.
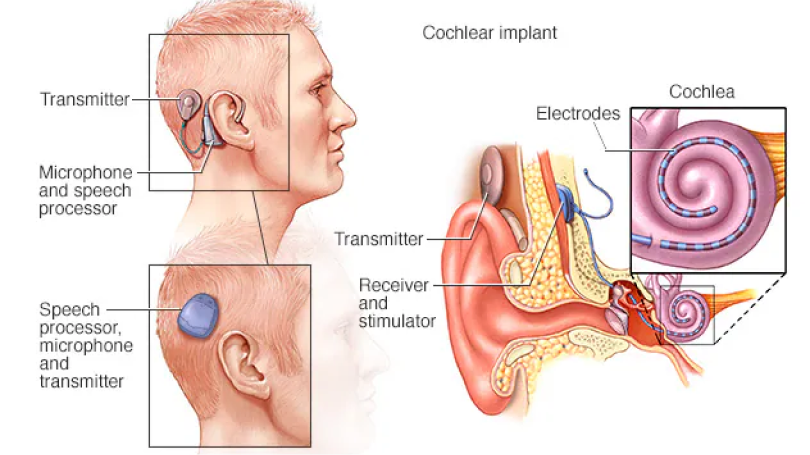
How cochlear implants work
A cochlear implant uses a sound processor that's worn behind the ear. The processor takes sounds from outside the ear. It sends the sound signals to a receiver that's been put under the skin behind the ear. The receiver sends the signals to electrodes that have been put in the snail-shaped inner ear, called the cochlea. The signals activate the cochlear nerve, which sends the signals to the brain. The brain hears those signals as sounds.
2 Main Devices
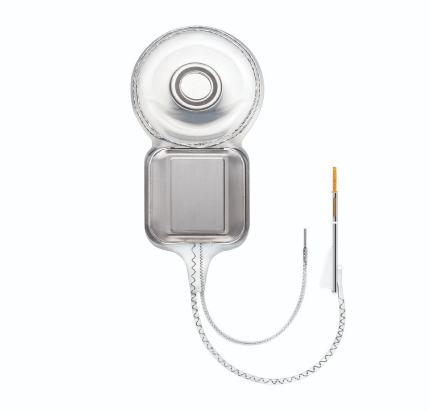
Internal Portion: Receiver
The internal device is implanted surgically and has a magnet, receiver, and an electrode array. The receiver is surgically placed under the skin behind the ear. The electrode array is inserted into the cochlea. More recent internal devices contain magnets which are MRI compatible.

External Portion: Speech Processor
The external portion – called the speech processor – can come in a variety of sizes and wearing options.
Standard features include:
- A battery is used to power both the external and internal portion.



WHAT IS
COCHLEAR IMPLANTS
A cochlear implant is a medical device designed to provide a sense of sound to individuals with severe to profound hearing loss. It works by directly stimulating the auditory nerve inside the cochlea (the inner ear) with electrical signals.
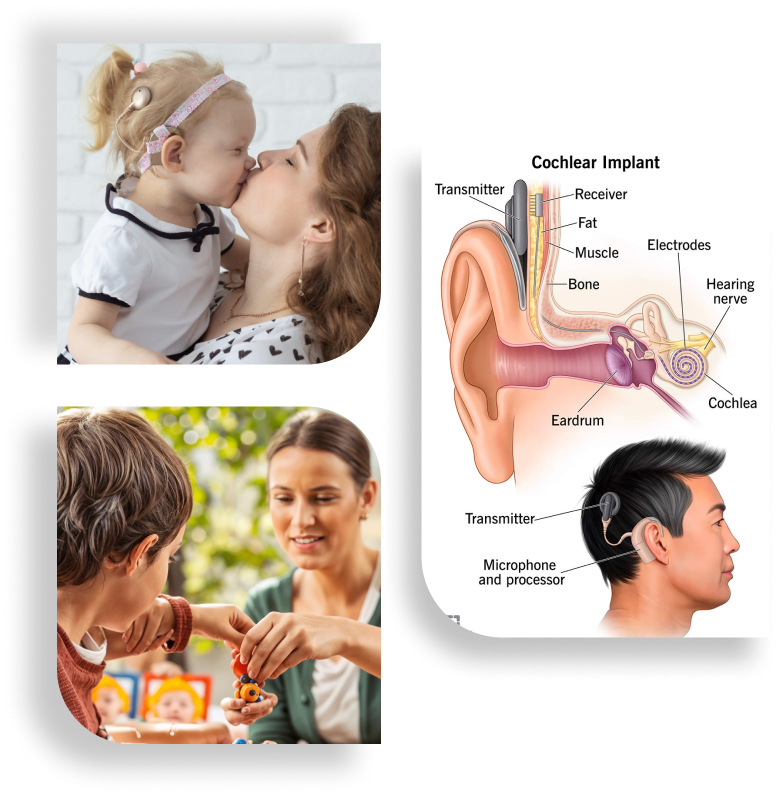
EVENTS
CIACS Dream Launch
Cochlear Implants Association & Charitable Society’s Dream Launch on 7/2/2016 at VJ Hall, Kothamangalam.
District meeting inaguration
District meeting inagurated by Rishi Augustin at Idukki Cherutoni.
WHO program in Delhi
Receives at Cochin International Airport after WHO program in Delhi.
LEADERSHIP
Navas
PresidentBiju R R
SecretaryAbdul Rasheed P A
TreasurerVijesh M
Vice PresidentNajumudheen P
Vice PresidentBaiju
Vice PresidentJoshy Michael
SecretaryFida Febin
Joint SecretarySreekumar
Joint SecretarySUPPORTING SCHEME
Supporting Scheme
Shruti Tharamgam
- The Government of Kerala launched the “Sruthitharangam (Cochlear Implantation Scheme)” under Kerala Social Security Mission by the Social Justice Department, Kerala.
- This scheme envisioned providing free cochlear implantation surgery for children in the age group of 0-5 years, who are hearing impaired.
- The early identification and intervention procedures initiated within six months of age should be the golden standard for the holistic development of a child with hearing loss.
- Cochlear Implant is a proven option for the treatment of profound hearing loss. The children from poor families whose annual family income is below ₹2 lakhs are eligible to get the benefit of this scheme.
- This scheme is implemented through Government as well as selected empaneled private hospitals in this field.
- The objective of this scheme is to provide a cochlear implant to children selected by Regional and State level technical committees for cochlear implantation and to provide financial support for Auditory Verbal Habilitation (AVH) to operate children through empaneled hospitals/centers.
Eligibility
- The child who is hearing impaired is eligible under the scheme.
- The child should be in the age group of 0-3 years.
- The annual family income of the applicant should be below ₹2 Lakhs
Dhwani Project
Dhwani is a government-initiated project in India aimed at providing follow-up treatment for individuals who have undergone cochlear implant surgery. This project was initiated in Kerala, India, and focuses on ensuring that patients receive the necessary care and support after the implantation procedure.
Key Objectives of Dhwani Project:
- Post-operative care: Providing comprehensive follow-up treatment to patients who have received cochlear implants.
- Financial assistance: Offering financial support for the maintenance and replacement of cochlear implant equipment.
- Awareness: Creating awareness about cochlear implants and their benefits among the general public.
- Rehabilitation: Supporting rehabilitation programs for patients to maximize the benefits of the implant.
By addressing these areas, the Dhwani project aims to improve the quality of life for individuals with hearing impairments and help them integrate into society.
Maintenance Scheme
A robust maintenance scheme is essential for the long-term success of a cochlear implant project like Dhwani. It ensures optimal performance of the device, minimizes complications, and maximizes the benefits for recipients.
- The municipality, panchayat, and corporation allocated 50,000 rupees per year and handed over the amount to the state health agency to address issues related to cochlear implants and ensure that recipients experience no problems with their implants.
Central Government
The Government of India's Assistive Devices for Individuals with Disabilities (ADIP) scheme provides free cochlear implants and post-operative rehabilitation for children with hearing impairments. The scheme is implemented by the Ali Yavar Jung National Institute of Speech and Hearing Disabilities (AYJNISHD) in Mumbai, which is an autonomous organization under the Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment's Department of Empowerment of Persons with Disabilities.
Under the revised ADIP Scheme, Cochlear Implants are provided to young children with severe to profound deafness in both ears. This modern technology allows these children to hear in one ear and, with post-surgery speech therapy, enables them to speak. The scheme covers children up to 5 years with congenital hearing loss and extends to children up to 12 years with post-lingual hearing loss. The government funds up to ₹6 lakh per child, covering the implant, surgery, mapping, and rehabilitation costs.
Cochlear Implants are procured by ALIMCO and distributed to empanelled hospitals by AYJNISHD. A total of 172 hospitals and 166 professionals are involved in the program. The country is divided into five zones for better project monitoring, with funds totaling ₹33.13 crore allocated from 2014 to 2017.
Eligibility
The ADIP Scheme provides cochlear implants for eligible children. To qualify, a child must:
- Be an Indian citizen
- Be 5 years old or younger as of December 31, 2021
- Have a 40% disability certificate as per the Persons with Disability Act
- Have a family income of ₹20,000 or less per month
After receiving the implant, recipients must visit the center for follow-up services, which include fitting, activation, adjustments, annual check-ups, and rehabilitation services.
ESI
The Employees' State Insurance (ESI) Scheme provides medical benefits to employees and their dependents, including cochlear implants for those with severe to profound hearing loss.
Eligibility
- Insured Person (IP) or Dependent: The individual must be an insured person (IP) under the ESI Scheme or a dependent of an insured person.
- Medical Condition: The patient must have severe to profound hearing loss in both ears, typically determined by an ENT specialist.
- Age Criteria: While age criteria can vary, typically, children up to a certain age (usually up to 5 years) with congenital hearing loss or older children with acquired hearing loss are eligible.
- Certification and Recommendation: A medical certification and recommendation from an ENT specialist are usually required to confirm the need for a cochlear implant.
- ESI Contribution Compliance: The insured person must be compliant with ESI contributions, meaning regular payments into the ESI fund as per the eligibility criteria of the scheme.
- Financial Eligibility: There may be specific financial limits or income criteria, though these are often covered under the broader ESI benefits without direct cost to the insured.
- Follow-Up Care: Post-surgery, the patient must comply with follow-up care, including regular check-ups, programming of the implant, and rehabilitation services, as required by the scheme.
The ESI Scheme typically covers the cost of the cochlear implant, surgery, and necessary follow-up services, provided the insured meets the eligibility criteria.
SURGERY CENTRES
Government Medical College

Kozhikode

Kottayam

Thiruvananthapuram
Empanelled List

Mesiarc ENT Hospital

Ascend ENT Hospital, Peinthalmanna

Noushad ENT, Ernakulam

Aster MIMS, calicut

SHA (State Health Agency)

SHA (State Health Agency)
@ Designed by The-Experiience

